-
 Call Now:
8010 552 552
7595 838 844
Call Now:
8010 552 552
7595 838 844
-
 Email Me:
[email protected]
Email Me:
[email protected]
Have you felt that something is stuck in your throat or there is difficulty in swallowing, even though you are not choking? This is not something to be ignored. It is a sign of a rare but serious disorder known as achalasia cardia.
It is a condition where the esophagus is unable to move food particles and liquids into the stomach. The disease mainly occurs when the myenteric nerve plexus of the esophageal wall deteriorates and loses its functional activity, thereby leading to deranged esophageal peristalsis.
Achalasia cardia can affect any individual at any age, though it is more common between the ages of 25 and 60 years. One might think that achalasia cardia is not that severe, but it’s a wrong notion. If not addressed at the right time, the difficulty in swallowing increases, which gradually makes an individual more prone to developing esophageal cancer.
Hence, recognising the symptoms and risk factors is important for receiving appropriate achalasia cardia treatment.
Achalasia cardia is a progressive disease. Patients with this condition experience a variety of symptoms that can be present all at once or develop slowly over time. The most common signs include the following:
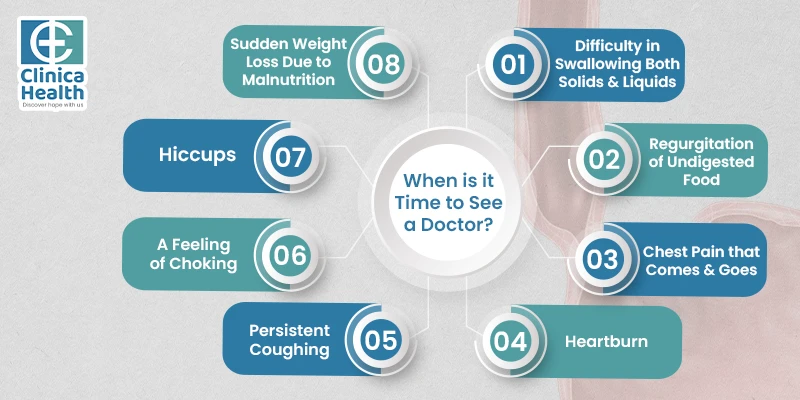
If you are experiencing these symptoms, it is essential to seek immediate medical attention promptly. Achalasia cardia treatment is a multidisciplinary approach and requires the expertise of a skilled doctor.
Healthcare professionals suspect various factors that develop this condition. Here are some of them.
Here are the following diagnostic procedures that your doctor might ask you to undergo to confirm the presence of achalasia cardia.
Achalasia cardia cannot be cured permanently. However, there are some effective ways to manage the condition effectively.
Pharmacotherapy: In this approach, doctors prescribe drugs to give relief from the symptoms. The two most common medicines that most patients are given include nitrates and calcium channel blockers. They need to be taken for a long time, and there can be a possibility of some side effects.
Botox injections: It is mostly suggested to patients who cannot tolerate invasive methods such as surgical myotomy or pneumatic dilatation. The effect in the initial months is around 80%–90%, though it decreases over time and individuals might require recurrent treatments.
Pneumatic Dilation: It is a non-surgical process. During the procedure, doctors use an air-filled balloon that dilates the lower sphincter muscles. The method is highly effective with a high success rate between 55-70 per cent per dilation.
Surgery: Among various surgical interventions, Laparoscopic Heller Myotomy (LHM) has now emerged as the preferred option by both patients and surgeons. It is a minimally invasive method that involves cutting the lower esophageal sphincter muscles (LES).
Esophagectomy: It is considered for patients who are in the advanced stage and are not responding to conventional treatments. It is a surgical intervention where some portion or all of the esophagus is removed.
Achalasia cardia is a lifelong condition. One must start the achalasia cardia treatment without delay to lead a healthy life. Also, discuss with your doctor about lifestyle and dietary measures that need to be taken to prevent further complications.